Verify out these metal parts china pictures:
The Soviet WWII Ground-Attack Aircraft Ilyushin Il-10 ‘Shturmovik’. Poland. 1945. Советский штурмовик Ил-10. Польша 1945 г.
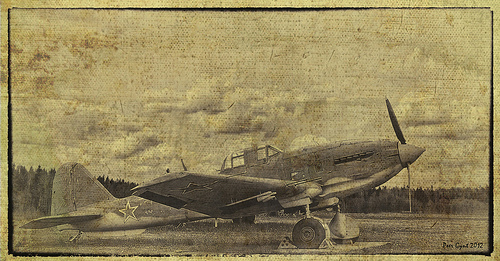
Image by Peer.Gynt
DIGITALLY COMPOSED IMAGE
The original aircraft is exposed in Central AirForce Museim, Monino.
Ilyushin Il-10 (Cyrillic Илью́шин Ил-ten, NATO reporting name: "Beast") was a Soviet ground attack aircraft developed at the finish of Globe War II by the Ilyushin construction bureau. It was also license-built in Czechoslovakia by Avia as the Avia B-33.
Improvement
From the start of Eastern Front combat in Globe War II, the Soviet Air Force (VVS) utilized the effective ground attack aircraft Ilyushin Il-two Sturmovik, powered by the Mikulin AM-38 inline engine. As the war progressed, the Soviets laid plans for that aircraft’s successor. The principal objective was to increase speed and maneuverability at low altitudes, primarily to evade tiny-caliber anti-aircraft artillery, which was the major threat for ground attack aircraft, and to eliminate some of the Il-2’s faults. The most promising project was a modern day, light and maneuverable close assault aircraft, the Sukhoi Su-six, developed by Pavel Sukhoi’s bureau from 1942. At the same time, Sergei Ilyushin developed a heavier aircraft, the VSh or Il-8 M-71, derived from the Il-two style, and on which it was partly based. Each projects were powered by the prototype M-71 radial engine, which did not enter production.
In 1943, Ilyushin began perform on a new aircraft, Il-1, which was to be a 1- or 2-seat heavily armoured fighter-interceptor, meant mainly for fighting enemy bombers and transports. The Il-1 was related to the Il-two design, but was much more contemporary, compact, and powered with a new Mikulin engine: the AM-42. But the VVS gave up the concept of heavy armoured fighters, due to their low speed, which was not enough to intercept contemporary bombers. As a result, Ilyushin decided to turn the Il-1 into a two-seat ground attack plane, with the designation changed to Il-10 in early 1944 (odd numbers had been reserved for fighters).
At that time, Ilyushin also finished a prototype of a heavier ground attack plane, the Il-eight, using the same engine, and a lot more closely derived from the Il-2. It carried a higher payload (1,000 kg/2,204 lb), but had decrease functionality than the Il-ten. Both sorts first flew in April 1944, the Il-10 proving significantly superior to the Il-8, which had poor handling. The Il-10 successfully passed trials in early June 1944.
The third competitor was a new variant of the Sukhoi Su-six, also powered by the AM-42 engine. After comparative tests, the Il-ten was deemed the winner and was chosen as the new ground attack plane, despite some opinions that the Su-6 was a better aircraft, notwithstanding inferior functionality and payload, with better gun armament. Notably, the Su-six prototype was tested with maximum payload, causing lowered efficiency, whilst the Il-ten was tested with regular payload. Some benefits of the Il-10 came from its technical similarity to the Il-2.
On 23 August 1944 the Il-10 was ordered into serial production by selection of the State Defense Committee (GKO) as a new ground attack plane.[five] Its armament was initially equivalent to late model Il-2s, with two 23 mm VYa-23 cannons and two ShKAS machine guns in the wings, and a 12.7 mm UBT machine gun for a rear gunner, and 400 kg, or a maximum 600 kg of bombs. As opposed to the Il-2 and Su-six, it was not initially meant to carry rockets.
Production of the Il-10 started in Kuybyshev’s factories No. 1 and No. 18. The very first production aircraft flew on 27 September 1944 and 99 aircraft have been produced by the finish of 1944. Early series aircraft showed teething troubles, most notably engine faults and fires. Most problems have been eliminated by 1945. Aircraft produced from April 1945 onwards could carry 4 unguided air-to ground rockets. Aircraft developed from 1947 onwards have been fitted with stronger armament, consisting of 4 23 mm NS-23 cannons in the wings and a 20 mm cannon for the rear gunner. Il-10 production ended in 1949, after a run of four,600 aircraft in the final two years, they were made in factory No. 64.
Between 1945 and 1947, 280 UIl-two or Il-10U trainer variants have been produced. The rear gunner’ cockpit was replaced with a longer instructor’s cockpit with dual controls. Its functionality and building had been equivalent to the combat variant apart from armament, which was lowered to two cannons, two rockets, and a standard load of bombs.
In 1951, the Czechoslovak firm Avia secured a license to make Il-10s, with the designation B-33. The very first one particular flew on 26 December 1951. Initially, their engines had been Soviet-constructed. From 1952 onwards the engines were also made in Czechoslovakia as the M-42. Besides the combat variant, a Czechoslovak trainer variant also entered service below the designation CB-33. In total, 1,200 B-33s had been constructed by 1956.
In 1951, due to encounter acquired throughout the Korean War, the Soviet Air Force decided that propeller ground attack aircraft may possibly still be valuable, and decided to renew Il-ten production in a modified variant, the Il-10M, which 1st flew on 2 July 1951. It was a bit longer, with a wider wingspan, and bigger handle surfaces, with a fin below the tail. Four of the more lately developed NR-23 cannons had been mounted in the wings, while the payload stayed the same, and newer navigation gear was installed, giving partial all-climate capability. Speed decreased slightly, but handling enhanced. Between 1953 and 1954, 146 Il-10Ms were produced, all but ten in Rostov-on-Don’s factory No.168.
In total, six,166 of all Il-10 variants were made, which includes those built beneath license.
Trials of Il-10s mounted with a lot more potent AM-43 and AM-45 engines took spot, but proved unsuccessful. Ilyushin next created a lighter close help aircraft, the Il-16, with improved performance and similar armament. It initial flew on ten June 1945. A short run entered production, but the project was cancelled in 1946 due to the AM-43 engine’s unreliability.
Technical description
The airframe featured a single engine, two-seat, monoplane, with a metal-covered frame. The plane was hugely armoured. The front portion of the fuselage, with the cockpit, was a shell of armour plates 4–8 mm thick the thickest, 8 mm, were below the engine, there was no armour above the engine. The front windshield was produced of armour glass 64 mm (two.five in) thick. Also armoured was: a roof above the pilot, side window frames in the pilot’s cab, a wall amongst crew seats, and a rear wall behind the cab. Total armour weight was 994 kg, which includes its attachment. The wing consisted of a central section, with two bomb bays, and two detachable outer panels. The undercarriage was retractable. The main wheels folded to the rear right after rotating by 86°.
Early Il-10s had two 23 mm VYa-23 autocannons (150 rounds each and every) and two 7.62 mm ShKAS machine guns (750 rounds every) fixed in wings, and a 12.7 mm UBT machine gun in a rear gunner station BU-eight, with 150 rounds. The horizontal angle of the rear machine gun field of fire was 100°. From 1947, the aircraft have been armed with 4 NS-23 23 mm cannons in the wings (150 rounds each and every) and 20 mm B-20T cannon in a rear gunner station BU-9 (150 rounds). The IL-10M had four 23 mm NR-23 cannons in wings (150 rounds every) and 20 mm B-20EN cannon in a rear gunner station BU-9M (150 rounds). Avia B-33 had four 23 mm NS-23RM cannons in wings and 20 mm B-20ET cannon in a rear gunner station BU-9M.
The typical bomb load was 400 kg, maximum load was 600 kg. This could be tiny fragmentation or anti-tank bomblets, place in bomb bays, or four 50–100 kg bombs in bomb bays and externally below wings, or two 200–250 kg bombs attached under wings. Modest bomblets have been place directly on bomb bay floors, in piles. A standard load was 182 (maximum 200) 2 kg AO-two,5-two fragmentation bombs, or 144 PTAB-2,five-1,five anti-tnk HEAT bombs. Apart from bombs, 4 unguided rockets RS-82 or RS-132 could be carried on rail launchers beneath wings. Avia B-33s were also fitted to carry other rocket kinds. Late Soviet aircraft could carry ORO-82 and ORO-132 tube launchers. In the tail section was a DAG-10 launcher with ten anti-aircraft or anti-personnel grenades AG-two (soon after getting thrown, they would fall with parachutes and then burst, but had been not extensively used in practice).
The Il-ten engine was a 12-cylinder inline V engine Mikulin AM-42, liquid-cooled, power: 1,770 hp continuous, takeoff energy: two,000 hp. Three-blade propeller AV-5L-24 of three.six m diameter. Two fuel tanks in the fuselage: upper 440 l more than engine, ahead of the cockpit, and decrease tank of 290 l under the cockpit. The aircraft had a radio set and a camera AFA-1M in a rear section of the fuselage.
Operational history
In October 1944, the Il-10 initial entered service with coaching units in the Soviet Air Force. In January 1945, the first Il-10 combat unit entered service with the 78th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment, but it did not enter action due to unfinished training. Nonetheless, 3 other Il-ten units managed to take element in the final combat actions of World War II in Europe. They were the 571st Assault Aviation Regiment (from 15 April 1945), the 108th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment (from 16 April 1945), and the 118th Guards Assault Aviation Regiment (on 8 May 1945). About a dozen aircraft have been destroyed by flak or engine breakdowns, but the Il-ten appeared to be a profitable style. One particular was shot down by an Fw 190 fighter, but a crew of the 118th Regiment shot down one more Fw 190 and probably damaged one more. On ten Could 1945, the day soon after the official Soviet finish of the war, (Victory Day), there had been 120 serviceable Il-10s in Soviet Air Force combat units, and 26 disabled ones.
Right after the USSR reentered the war against the Empire of Japan, with the invasion of Manchuria, from 9 August 1945, one particular Il-ten unit, the 26th Assault Aviation Regiment of the Pacific Navy Aviation, was utilised in combat in the Korean Peninsula, attacking Japanese ships in Rasin and rail transports.
Right after the war, until the early 1950s, the Il-10 was a basic Soviet ground attack aircraft. It was withdrawn from service in 1956. At the very same time, operate on new jet-powered devoted armoured ground attack planes (like the Il-40) was canceled, and the Soviets turned to multipurpose fighter-bomber aviation. The Il-10 and its licensed variant, the Avia B-33, became a standard ground attack plane of the Warsaw Pact nations. From 1949 to 1959, the Polish Air Force utilised 120 Il-10s (including 24 UIl-ten), and 281 B-33s. In Poland, the B-33 was modified to carry 400 l fuel tanks below its wings. From 1950 to 1960, Czechoslovakia utilized 86 Il-10s, including six UIl-10s, and about 600 B-33s. From 1949 to 1956, the Hungarian Air Force utilised 159 Il-10s and B-33s. From 1950 to 1960, the Romanian Air Force utilised 14 Il-10s and 156 B-33s. Bulgaria also utilized these aircraft.
In the late 1940s, 93 Il-10 and UIl-10s had been offered to North Korea. They had been then used in the 57th Assault Aviation Regiment throughout the early phase of the Korean War. They have been initially utilised with achievement against the weak anti-aircraft defense of South Korean forces, but then they suffered heavy losses in encounters against the USAAF fighters and have been bombed on the ground themselves. Right after numerous weeks, about 20 remained. In the summer season of 1950, North Korea received more aircraft from the USSR. The North Koreans claimed to sink a warship on 22 August 1950 with Il-10s, but it was in no way confirmed.
From 1950, Il-10s have been employed by the People’s Republic of China, in two regiments of an assault aviation division. They had been employed in combat in the course of a conflict with the Republic of China, (Taiwan), over border islands in January 1955. They remained in service till 1972. From 1957, Yemen employed 24 B-33s.
General traits
Crew: two, pilot and gunner
Length: 11.12 m (36 ft six in)
Wingspan: 13.40 m (44 ft)
Height: four.10 m (13 ft five in)
Wing area: 30 m2 (322.9)
Empty weight: 4,675 kg (10,305 lb)
Loaded weight: 6,345 kg (14,000 lb)
Max. takeoff weight: six,537 kg (14,410)
Powerplant: 1 × Mikulin AM-42 liquid-cooled V-12, 1,320 Kw (1,770 hp)
Performance
Maximum speed: 550 km/h at 2,700 m 500 km/h at ground level (340 mph at 8,860 ft / 310 mph)
Range: 800 km (500 mi)
Service ceiling: 4,000 m (13,123 ft)
Wing loading: 211 kg/m2 (43.two lb/ft2)
Armament
two × 23 mm Nudelman-Suranov NS-23 auto cannons in wings, 150 rounds per gun
two × 7.62 mm ShKAS machine guns in wings, 750 rounds per gun
1 × 12.7 mm UBST machine gun in the BU-9 rear gunner station, 190 rounds
Up to 600 kg (1,320 lb) of numerous weapons as described in the text.
Wikipedia